Introduction
In the current digital era, cloud computing has become an essential tool for companies looking to innovate and simplify their processes. However, shifting to the cloud also brings a new set of security problems. Some businesses have continued to use poor safety and security protocols in spite of how important it is to secure cloud environments; this has left them open to a variety of cyberattacks. The data, systems, reputation, and cloud security aspects of an organization can all be seriously impacted by these cloud threats, which can range in complexity from phishing attempts to highly advanced malware. For this reason, Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) has been developed to help businesses maintain a safe and secure cloud environment. We will discuss the key components of CSPM, its importance, and recommended implementation techniques in this educational blog post.
Overview of CSPM
One security tool that helps businesses determine whether their cloud infrastructure is configured securely and compliantly is called Cloud Security Posture Management( CSPM). CSPM technologies automatically monitor risk in the security settings and configurations of public cloud services by analyzing and evaluating the environment settings and configurations. Cloud security is prioritized by CSPM, which gathers configuration data from existing cloud services and continuously checks the configurations for risk. To keep their cloud infrastructure as safe and secure as possible, businesses must utilize cloud security posture management (CSPM). By executing strict access controls, continuously detecting and solving misconfigurations, and actively monitoring regulatory requirements, CSPM guarantees the protection of a business's digital assets.
What Causes Misconfigurations?
Developers can easily change access control of a particular cloud resource or make certain ports open in the firewall. This process's simplicity has a drawback in that it makes misconfigurations much more likely to happen. As businesses struggle to identify and manage a large number of accounts, their configuration, assigned permissions, and resources, multi-cloud environments also limit visibility.
Many times, misconfigurations occur due to a lack of understanding of how cloud resources work and the specific security measures needed. Because of this, cloud security problems may go unnoticed, making them exposed to cyberattacks.
For example, when an S3 bucket is created, it automatically disables configurations that allow public access. However, if this configuration is unintentionally left open, it could expose sensitive data stored in the bucket. A similar incident occurred in 2020 when millions of Clubhouse users' private information was exposed due to a misconfigured Amazon S3 bucket.
This is not the only case, as misconfigurations can also happen due to a disabled MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) feature. Multi-factor authentication is a safe authentication technique that verifies users using two factors. These factors may consist of a security question, location, biometric information,OTP, credentials, and more. Multi-factor authentication helps to prevent system access for attackers who manage to obtain a user's credentials.
However, if this vital feature is unknowingly disabled, it may result in unauthorized access or data breaches. Imagine a scenario where an employee accidentally disabled MFA on their cloud storage account. This could potentially allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data, even if other security measures are in place.
There is not a major incident that happened solely due to a disabled MFA. While MFA plays a crucial role in preventing unauthorized access, it's often part of a larger security breach or a combination of factors that contribute to an incident.
- Capital One data breach (2019): A misconfigured web application firewall allowed attackers to bypass security measures and access sensitive customer data, even though MFA wasn't explicitly disabled.
- The Target data breach (2013): It involved a combination of factors, including stolen credentials and disabled MFA on specific accounts. While not the sole cause, the lack of MFA likely amplified the attacker's access and the scope of the breach.
These incidents emphasize the importance of proper configuration for all security tools.
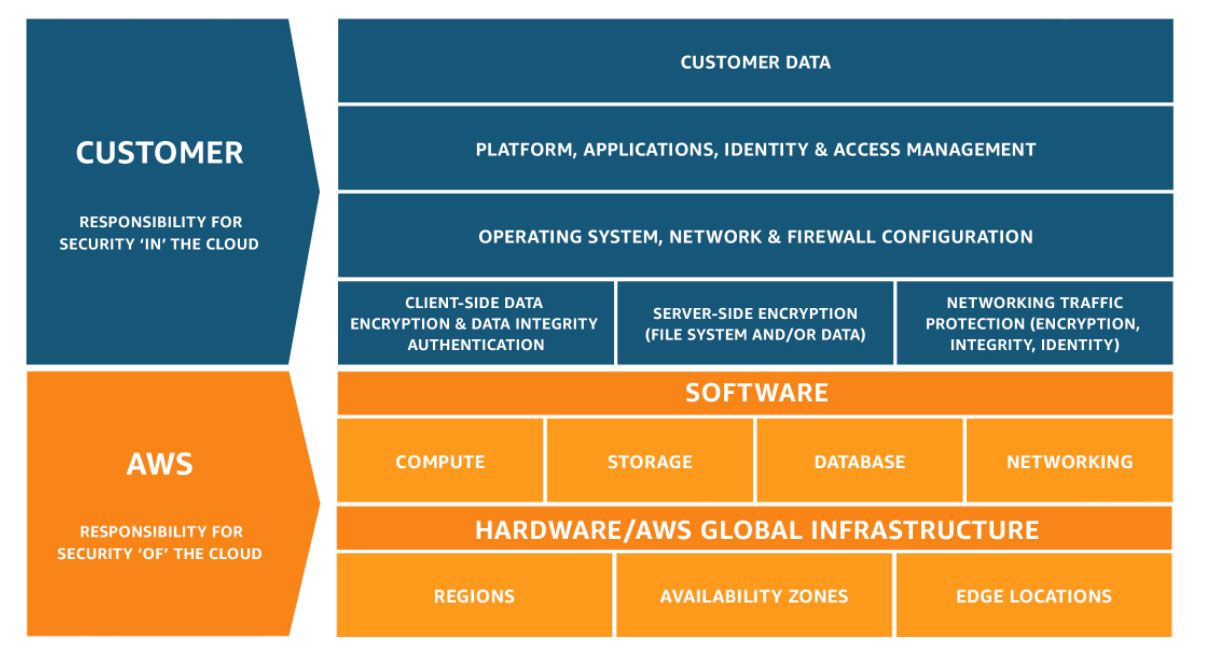
Shared Responsibility Model For Cloud Security
There is a common misconception that cloud service providers handle cloud security automatically. In reality, though, workload and data security is a shared responsibility between the user's organization and the cloud service provider.
Cloud environments differ from traditional data centers, where an organization bears full responsibility for the infrastructure security. Instead, this responsibility is shared by the company and the cloud service provider.
Although every cloud service provider has a different shared responsibility model, they should all make clear what each party is responsible for.
Under AWS's shared responsibility model for cloud security, a customer's level of responsibility is determined by the cloud service they use. For example,
Key Capabilities Of CSPM
Security
CSPM helps companies prepare for security threats by finding and fixing errors, including vulnerabilities or misconfigurations, in their cloud environment.
Compliance
By improving security and preventing unfavorable outcomes like data breaches, CSPM helps companies follow guidelines.
- Visibility
CSPM helps businesses make better decisions about their security plan by offering helpful information about the overall security aspect of cloud environments.
CSPM Features
- Continuous monitoring of cloud environments to detect any misconfigurations or vulnerabilities.
- Automatically address potential security issues through pre-set, customizable actions.
- Implements security policies and best practices within the cloud environment.
- Provides detailed reports on both compliance status and overall security aspects.
Comparison of CSPM with other Security Tools
In addition to above mentioned powerful features, knowing how CSPM compares to other security tools in your security ecosystem is essential.
| Features | CSPM | Cloud Access Security Broker(CASB) | Cloud Workload Protection Platform(CWPP) | Cloud Identity and Entitlement Management(CIEM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Cloud Infrastructure and Configuration. | Identity and Access Management. | Workload Security. | Identity Governance and Entitlement Management. |
| Strengths | Visibility, Misconfiguration Detection, Policy Application. | Data Leak Prevention. | Threat Detection. | User Behaviour Monitoring. |
| Complementary | Provides insights for CASB and CWPP policies | Can use CSPM findings for data control. | Frequently combined with CSPM for reliable security. | Strengthens Identity security within CSPM view. |
Tools like CASB concentrate on securing data access and movement, whereas CSPM is excellent at managing infrastructure security. In addition to CSPM, CWPP explores more workloads. With its focus on entitlement management and identity governance, CIEM offers vital insights into user entitlements and dangers. These aren't replacements; instead, they function best when used in combination with layered security.
CSPM Benefits
- In multi-cloud environments, with simple dashboards that let you investigate individual threats and efficiently prioritize remediation efforts, you can get real-time visibility into your entire cloud security posture. Security teams will find it simpler to swiftly detect and fix system flaws and configuration errors.
- Threats are immediately identified by CSPM tools for all cloud-native deployments. By using constant monitoring to find unauthorized access and activity, they enable organizations to prevent attempted cyberattacks and insider threats.
- In addition to threat detection, automated response capabilities are utilized to prevent security risks from getting worse in advance. To quickly contain incidents, pre-established workflows are initiated, suspicious activity is blocked, and compromised accounts are isolated.
Practical Use Cases:
- In order to stop a data breach, a significant online retailer used CSPM to locate and close an open S3 bucket containing customer data. The constant scanning of cloud environments by CSPM finds misconfigurations like open S3 buckets. Because it notified them of the situation, the retailer was able to close the open bucket and prevent a potential data breach.
- Using CSPM, a financial services company was able to minimize potential economic losses from cyberattacks by quickly and efficiently fixing vulnerabilities found in their cloud infrastructure. In order to reduce possible financial losses, it helped the financial services company promptly identify and fix vulnerabilities.
Including cloud security posture management (CSPM) in your security strategy is vital as cloud environments get more complicated. With a focus on cloud security, OptimoSecurity offers robust solutions to take advantage of the benefits mentioned in this blog. Your cloud infrastructure is safe and compliant, thanks to its features like automatic compliance adherence, continuous monitoring, and an auto-correction engine that fixes the threat anomaly immediately.
By following best practices, CSPM enables you to improve your security aspects, reduce risks, and optimize costs.
Don’t overlook this critical tool for ensuring the security and compliance of your cloud assets.